Cellular. How to choose a mobile operator? Mobile network for example in case
It is interesting! Acidants-inventors ahead of the caricateur Lewis Baumer. Panch magazine (1906) has published the people who have used portable telephone models by Hyde. The plot was entitled "Expectations 1907".
Phones developed in parallel broadcasting, communications. The first attempt to create a wireless model has been taken (1908) joint efforts:
- Professor Albert Jancla.
- Transcontinental telephone company Auckland.
- Power company.
Railways
Mass production of portable radio stations burned. Since 1918, a section of Berlin-Zosssen of German railways tests cordless phones. Six years later, Berlin-Hamburg line provided private passengers a similar service. 1925 consider the indivisal point of industrial manufacture. Now first class passengers can call subscribers while enjoying the charms of the trip.
The first portable radio stations of the 40s weighed pretty, more reminding the solid sizes of the backpack. The United States (Sant Louis, Missouri) began to develop commercial samples on June 17, 1946. Soon, AT & T announced a mobile phone service (MTS). Several scattered local operators were born.
Says Moscow!
Soviet engineer Leonid Kompyovich (1957-1961) introduced the first instances of devices. The weight of the model was 70 g, fully allowing the housing to be selected palm. The government, the urgency of the Muscovite's effort, gave priority to the development of the automotive version "Altai", designed to equip the heavy life of the managers. The equipment constructed by the Voronezh Scientific Institute of Communication included MRI-1327, the trial version covered the capital (1963). In 1970, 30 cities were able to communicate. The type of radio communications exists in Russia.
The capital exhibition INFORGA-65 presented the labor of the Bulgarian company Radioelectronics. The idea is used today: dividing the transceiver equipment. A basic station performs hard work, a relatively small tube allows the subscriber to speak within the territorially limited area. The design used the ideas of Kupriyanovich. One base served as a reference point to the maximum of 15 subscribers. 1966 The output of the commercial version of the RAT-0,5 served by the RATZ-10 access point is marked.
Mobile telephony straight displays the 0G standard, used by the originating company MTS.
First operator
So, since 1949, mobile telephone service begins to operate. Initially (1946), preceding the formation of the unit, AT & T began to equip the United States. After a couple of years, thousands of cities, high-speed trails received the benefits of civilization. However, the number of subscribers was 5,000. Weekly committed 30,000 calls. Hand switching channels by the operator. The weight of the speaker's equipment was 80 pounds.

Initially, the company provided three frequency channels, allowing simultaneously to talk ... Three subscribers of the city. Cost:
- 15 dollars monthly.
- 30-40 cents per call. Given inflation, the modern subscriber will pay $ 3.5-4.75.
The UK service named post offices service named. In 1959, the network covered the neighborhood of Manchester, six years later, Powethel was wrapped in London. Then the connection of the main cities of the kingdom followed. Operators gradually increased the speed of the trash in place. IMTS added frequency channels, simultaneously reducing the initial 35 kg of equipment weight. The total number of US subscribers reached 40,000. Two thousand New Yorks divided 12 channels. Wishing to make a call had to wait for half an hour.
RCC
Radio Common Carrier is considered the main competitor of MTS. The service successfully littered the ether of 20 years (60-80s). The AMPS systems have made the company's equipment outdated. There was no roaming concept due to the incompatibility of standards:
- Two-tone sequential pagination of the incoming call.
- Tone set.
- SECODE 2805 (tone of the call of 2.805 kHz, resembling the principle of operation of MTS equipment).
Part of the phones involved half-duplex mode (Motorola Lomo), the other - more resembled the radio (series 700 RCA). Omaha's mobile phone was becoming breasting iron in Arizona. RCC ignored technical progress until competitors developed roaming concepts.

Since 1969, the Central Railway Penn supplied the train line New York - Washington by mobile radio stations. The system received 6 channels of the DMW range of 450 MHz. British rabbit system developed the concept of Bulgarian scientists. The maximum range of the subscriber base station was 300 feet (100 meters). Now a similar technology that uses 4G is launched by Apple.
The list of significant cellular operators of the second half of the XX century
- Norwegian OLT (1966).
- Finnish ARP (1971). First commercially successful project. Researchers refer to 0G equipment.
- Swedish MTD (70s).
- British Radicl (July 1971).
- German A-Netz (1952), B-Netz (1972).

Automotive Swedish MTA (1956), developed by the sturgeon lauren (speaker) used a pulse set. Outgoing calls were straight, the neglence station was chosen by the operator. Equipment team:
- Ericsson switches.
- Apparatuses, basic stations Radiaactibolage (SRA) and marconi.
The hull womb is full of relay, vacuum lamps, weight is 40 kg. 1962 brought relief, Javiling the second generation of services V. Transistors reduced weight, the DTMF alarm system unloaded resources. 1971 is marked by the appearance of MTD. The resource existed for 12 years, leaving the orphans of 600 subscribers.
Development of the Concept of Cellular Communications
World War II ended with the complete lack of standards, frequencies, isolated channels. Cold December 1947 Douglas Ring, Rae Young, Bella Lab Engineers, put forward the idea of \u200b\u200ba cellular cell. Two decades later Richard Frenkel, Joel Engel, Philip Porter developed a concept, developing a detailed plan. Porter stressed the need to use towers equipped with directional antennas. The highlighted main petal sharply reduced the level of interference. Porter first put forward the concept of providing resources on request, reducing the number of collisions.
Early experiments excluded the possibility of an operational change of honeycomb. Principles of reuse of frequency, handover, the basics of modern communication are laid in the 60s. Laboratory engineers Bella, Amos and Joel Jr., invented (1970) three-sided networks, simplifying Handover. The subscriber switching plan was discussed (1973) by Floom and Nussbaum, the alarm system - Hahenburg.

Predecessors preferably flared by the equipment designed to please the transport workers. On April 3, 1973, Marty Cooper (Motorola, USA) constructed the first manual version, immediately calling the competitor to Dr. Joel Engel (Bella Lab). The weight of the device is 23 cm long, 13 cm wide, a thickness of 4.45 cm was 1.1 kg. The battery charged 10 hours, providing 30 minutes of full communication. Cooper's chief played a key role, attracted the attention of Motorola's leadership.
Communication generations
The development of the industry went pronounced waves. The term generation will overtake the race at step 3G. Now the word is used retrospectively, overlooking the former merit.
1G - Analog cells
The concept is launched (1979) by the Japanese company Nippon Telegraph and Phone (NTT), covering Tokyo Metropolis. After completing the plan of the five-year plan, engineers were covered with a mesh of the island of the archipelago. 1981 is considered a year of birth of the Danish, Finnish, Norwegian, Swedish NMT communication systems. The unified standard helped implement international roaming. The United States waited 2 years, seeing European successes. Then the Chicago Provider of Amerity, using Motorola's devices, began capturing the market. Similar steps from Mexico, Canada, Great Britain, Russia followed.
North America (October 13, 1983 - 2008), Australia (February 28, 1986, Telecom), Canada widely used AMPS; United Kingdom - TACS; West Germany, Portugal, South Africa - C-450; France - radioka 2000; Spain - TMA; Italy - RTMI. The Japanese raised standards incredibly quickly: TZ-801, TZ-802, TZ-803. NTT's competitor has created a JTACS system.
The standard includes a digital call call, however, the transmission of information is fully analog (modulated DMW signal above 150 MHz). Encryption was absent completely, stinging the coin of pockets of private detectives. Frequency division of channels left the place of illegal cloning of devices.

On March 6, 1983, the development of the Dynatac 8000x Mobile Physics was launched, the company worth the company. A whole decade The device was raised to reach the store stores. The list of people willing to subscribe was calculated by thousands of individuals, despite the obvious disadvantages:
- Battery life.
- Dimensions.
- Fast discharge.
The generation of phones later successfully upgraded, providing an upgrade to 2G generation.
2G - digital communication
The appearance of the second stage of development marked the beginning of the 90s. We immediately marked two main competitors:
- European GSM.
- American CDMA.
Key differences:
- Digital information transmission.
- Outflowing tower call with telephone.
Era 2G is called the era of ordered phones. Buyers too much, the manufacturer collected the wishing lists in advance. The first radio network launched Finland. European frequencies are historically higher than the American, some ranges 1G and 2G (900 MHz) are superimposed. Outdated systems were accelerated. American IS-54 captured previous resources AMPS.
IBM Simon is customary to be the first smartphone: mobile phone, pager, fax, PDA. The program interface provided a calendar address book, clock, calculator, notepad, email, the prediction option of the next symbol like T9. Touchscreen provided QWERTY keyboard control. The kit supplemented the stylus. PCMCIA memory card with a capacity of 1.8 MB expanded functionality.

There has been a tendency to minimize the devices. Bricks began to weigh 100-200 g. First assessed by the public of SMS messages. The first (generated automatically) GSM text was sent on December 2, 1992, in 1993 - people were opposite. The batch prepayment method soon made SMS to communicate popular youth fun. Later, passion covered older generations.
The emergence of mobile payments (Coca-Cola, Parking machines), the release of a paid media system was marked by 1998: the first ringtone was sold to the Radiolin Provider (now Eliza). Initially, news subscriptions (2000) distributed free of charge, the service was paid for advertising contributions to sponsors. Customer-Bank (1999, Philippines), supported by GLUB operators, smart access appeared. Then the Japanese NTT Docomo has implemented telephone Internet.
3G.
Generation 2G ended with a total victory mobile technology. The daily life of billions was filled with challenges. An innovative idea designed to increase the data transfer rate was switching packets (instead of switching channels). The developers released the leaders to manufacturers, concentrating entirely on consumer qualities. The resulting consequence of the introduction of the host of standards. Compatible CDMA introduced several improvements:
- Reducing the connection time of the connection.
- Increase batch speed (3.1 Mbps).
- Flags QoS.
- Simultaneous use of a temporary slot by several subscribers.
The first network of 3G WCDMA (May 2001, commercial use, starting on October 1) covered Tokyo. South Korean competitors (KTF, SK Telecom) were waiting for 2002. CDMA2000 1xEV-Do technology reached the US banks, and the coin operator managed to go bankrupt. In parallel, Japan acquired the second set of bees cells, thanks to Vodafone. The global introduction of technology followed.

In parallel, the intermediate stages of the formation of systems - 2.5; 2,75g, for example, GPRS. These funds provided part of the requirements of 3G, the missing others: CDMA2000-1x is theoretically able to give 307 kbps. Following goes eDGE technologynominally corresponding to 3G. Practically maximum thresholds are unattainable due to the presence of interference.
Gradually, the television and radio company was aware of the possibilities of wireless digital broadcasting. The first birds flew through Disney, RealNetWorks. Evolution appeared to the world of HSDPA (high-speed downward batch access) - an improved HSPA version. The standard was recognized as equal to 3.5G, marketers happily used the abbreviation 3G +. The current version supports 1.8 data loading rates; 3.6; 7.2; 14 Mbps. At the outcome of the 2007 full 295 million subscribers operated the network everywhere, accounting for a share of 9% of global demand for communication services. Super profits ($ 120 billion) forced phone manufacturers immediately upgrade production conveyor: adapters, PC consoles.
4G.
The results of 2009 dismissed: a new generation change is made, caused by the growing requests of the public. They began to search for technologies, ten times raising transmission rates. The first swallows are WiMAX technology, LTE.

Infection lightningly covered Scandinavia, thanks to the efforts of the Teliansonera. Network switching is removed irrevocably, replaced with IP addressing. ITU runts (March 2008) area:
- Game applications.
- IP telephony.
- The Internet.
- HDTV.
- Video conferencing.
- Three-dimensional broadcasts.
Installed speeds:
- 100 Mbps - mobile objects (transport).
- 1 Gb / s - Typical mobile applications.
Given said, belonging to LTE communication types, WiMAX to 4G is doubtful. Experts stated the principled inability to achieve the technologies of the established plank. LTE-A nominally touched the fronting, having failed torture tests. Engineers lay hopes for WirelessMan-Advanced developed. One align everywhere: Engineer works, the marketer is praised. So the world is arranged.
Operating principle
Cell networks exploit access control ideas (Mac). Full analogue wired version. Multiplexing data occurs, ensuring resource savings. The specific design of the protocol determines the physical environment. Radio signal changes optical effects, weather conditions, time of day, year. The quality of reception is constantly fluctuating. An obvious solution is an increase in capacity, but the measure simultaneously enhances the interference phenomenon. The number of errors is growing. Approximate relations:
- Wired network - the number of errors of less than a million lobe.
- cellular - The number of incorrect packages over a thousandth share.
The difference exceeds three orders. Terminals have to use half-duplex mode. The energy of the transmitted package is much higher than the received signal. Features of the circuitry admittance. Separation of such a high power into the tract of receiving a full-duplex device interferes with packet decoding.
Scheme with controlled access
The controller of operations is assigned, which coordinates the distribution of resources. More often, the role is executed, the access point. The terminal performs a predetermined channels, frequency, time slots, antennas. Guaranteed the absence of conflicts.

- TDMA. Temporary division.
- FDMA. Frequency division.
- OFDMA. Orthogonal access in frequency.
- SDMA. Spatial division.
- Poll.
- Token Ring.
Dynamic resource allocation gives indisputable benefits hardly loaded networks. Because protocols with free access lion's time spend, preventing collisions. The terminal checks the alternately activity of subscribers using the random number algorithms, providing those who want to transfer the information slots.
The most common mobile communication type is a cellular communication. Cellular services are provided by subscribers by operators.
Wireless communication cell phone Provides a network of base stations.
Each station provides access to a network in a limited area, the area and the configuration of which depends on the terrain and other parameters. Overlapping coating zones create a structure like bee honeycombs; From this image and the term "cellular communication" occurs. When you move the subscriber, the phone is serviced by one one, then another base station, and switching (change of cell) occurs in automatic mode, completely imperceptibly for the subscriber, and does not affect the quality of communication. This approach allows using low-power radio signals to cover the mobile network with large areas, which provides this type of communications, in addition to efficiency, also a high level of environmental friendliness.
The operator's company not only technically provides a mobile communications, but also enters into economic relations with subscribers who acquire some set of basic and additional services. Since the types of services are quite a lot, the rates for them are combined into the kits, referred to tariff plans. The calculation of the cost of the services provided to each subscriber is engaged in the bilingual system (software and hardware system, leading the accounting of services provided to the Subscriber and services).
The billing system of the operator interacts with similar systems of other companies, for example, providing the subscriber of roaming services (the opportunity to use a mobile communications in other cities and countries). All mutual settlements for mobile communications, including in roaming, the subscriber produces with its operator, which is for it a single settlement center.
Roaming - access to mobile communication services outside the coating zone of the "home" operator network, with which the subscriber has a contract.
Being in roaming, the subscriber usually saves his telephone number, continues to use his cell phone, making and taking calls just as in the home network. All the necessary action for this, including the interference traffic exchange and attracting resources of other communication companies as necessary (for example, providing transcontinental communications), are automatically produced and do not require additional actions from the subscriber. If the home and guest network provide communication services in different standards, roaming is still possible: another machine can be issued to the subscriber during the trip, while saving its phone number and automatically routed calls.
The history of cellular communication.
Work on the creation of civilian mobile communication systems began in the 1970s. By this time, the development of ordinary telephone networks in European countries has reached such a level that only the availability of telephone communications could be the next step in the evolution of communications everywhere.
Networks on the first civilian communication standard - NMT-450 - appeared in 1981. Although the name of the standard is a reduction in the words of Nordic Mobile Telephony ("Mobile telephony of the Nordic countries"), the first on the planet cellular network was deployed in Saudi Arabia. In Sweden, Norway, Finland (and other countries of Northern Europe), NMT has earned a few months later.
Two years later - in 1983 - on the territory of the United States was launched the first network of AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone Service), created in the Research Center Bell Laboratories.
NMT and AMPS standards, which are customary to the first generation of cellular communication systems, provided for data transmission in analog form, which did not allow the proper level of noise immunity and protection against unauthorized connections. Subsequently, they have enhanced by the use of digital modification technologies, for example, DAMPS (the first letter of abbreviation with its appearance, is obliged to the word Digital - "digital").
Second-generation standards (so-called 2G) - GSM, IS-95, IMT-MC-450, etc., initially created on the basis of digital technologies, exceeded the first generation standards for sound quality and security, as well as, as it turned out later, on the mortgaged in standard development potential.
Already in 1982, the European Conference of Email and Telecommunication Administrations (CEPT) has created a group to develop a single standard of digital cellular communication. GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS).
The first GSM network was commissioned in Germany in 1992. Today GSM is a dominant standard of cellular communication both in Russia and around the world. In 2004, in our country, the GSM network served over 90% of cellular subscribers; In the world, GSM used 72% of subscribers.
For operation of the GSM standard, several frequency ranges are isolated - they indicate numbers in the names. In the European Region, GSM 900 and GSM 1800 are mainly used, in America - GSM 950 and GSM 1900 (at the time of the approval of the standard in the United States "European" frequencies there were engaged in other services).
Popularity GSM standard has provided its meaningful features for subscribers:
- protection against interference, interception and "twins";
- the presence of a large number of additional services;
- the opportunity in the presence of "add-ons" (such as GPRS, EDGE, etc.) provide data transmission with high speeds;
- presence in the market of a large number of telephone sets operating in the GSM networks;
- Easy to change one apparatus to another.
In the process of development, the cellular networks of the GSM standard have gained expansion opportunities at the expense of some "add-ons" above the current infrastructure that ensure high-speed data transmission. GSM networks with GPRS support (General Packet Radio Service) received a name of 2.5G, and the GSM network with EDGE support (Enhanced Data Rates for Global Evolution) is sometimes called 2.75G networks.
In the late 1990s, third-generation networks appeared in Japan and South Korea (3G). The main difference between the standards on which 3G networks are built, from predecessors - advanced high-speed data capabilities, which allows you to implement new services in such networks, in particular, video telephony. In 2002-2003, the first 3G commercial networks began to work in some countries of Western Europe.
Although the 3G network currently exists only in a number of regions of the world, work in the engineering and technical laboratories of the largest companies is already underway to create a cellular standards of the fourth generation. At the same time, it is not only a further increase in the data transfer rate, but also improving the efficiency of using the bandwidth of frequency ranges allocated for mobile communications to access the services could a large number of Subscribers located in a limited territory (which is especially relevant for megalopolises).
Other mobile communication systems.
In addition to cellular communication, today there are other civil communication systems that also provide mobile communications on radio channels, but built on other technical principles and oriented to other subscriber terminals. They are less common than cellular communication, but they are used when the use of cell phones is difficult, impossible or economically unprofitable.
The DECT microspose standard is becoming increasingly popular, which is used for communications in a limited territory. The base station of the DECT standard is capable of providing tubes (they can be serviced to 8 at the same time) communication, call forwarding, and access to the public telephone network. The potential of the DECT standard allows you to provide mobile communications within urban microdistrics, individual companies or apartments. They are optimal in the regions with low-rise buildings whose subscribers only need voice communications and can do without mobile data and other additional services.
In satellite telephony, base stations are located on satellites located in near-earth orbits. Satellites provide a connection where the deployment of the usual cellular network is impossible or unprofitable (in the sea, on the extensive small-populated territories of the tundra, desert, etc.).
Transitnet networks providing subscriber terminals (they are not called non-telephones, but radio stations) in the limits of a certain territory, are systems of base stations (repeaters) that transmit radio signal from one terminal to another with their significant distance from each other. Since trotking networks usually provide communication to employees of departments (MIA, MES, " Ambulance"Etc.) or on the technological sites of a large size (along the highway, at a construction site, in the factories, etc.), then the trunking terminals do not have entertainment and design sizes in the design.
Wearable radio stations establish communication with each other directly, without intermediate communication systems. Mobile connection of this type prefer as government (militia, fire protection, etc.) and departmental structures (for communications within the warehouse complex, parking or construction site) and individuals (mushrooms, fisherman hunters or tourists), in situations When it is easier and cheaper to use pocket radio stations to communicate with each other than cell phones (for example, in remote areas where there is no coating of cellular networks).
Padzhing communication provides short messages to subscriber terminals - pagers. Currently, paging communications in civil communication are practically not used, because of their limitations, they are supplanted to the area of \u200b\u200bhighly specialized solutions (for example, serve to alert personnel in large medical institutions, data transfer to information electronic scoreboard, etc.).
Since 2004, a new subspecies of mobile communications is increasingly widespread, providing high-speed radio channel data transmission (in most cases, the Wi-Fi protocol is used for this). Wi-Fi-coating areas available for public use (paid or free) are called hot spot. Subscriber terminals in this case are computers - both laptops and PDAs. They can provide a bilateral voice connection via the Internet, but this feature is extremely rare, mainly the connection is used to access the most common Internet services - email, websites, instant messaging systems (for example, ICQ), etc. .
Where Mobile Communication is moving.
In developed regions, the main focus of the development of mobile communications for the near future is the convergence: providing subscriber terminals of automatic switching from one network to another with the aim of the most efficient use of the capabilities of all communication systems. Save subscriber tools and improve communication quality will allow automatic switching, for example, with GSM on DECT (and back), from satellite communication to "ground", and when providing wireless data transmission - between GPRS, EDGE, Wi-Fi and other standards, many Of which (for example, WiMAX) only expect an hour.
Mobile place in the global economy.
Communications are the most dynamically developing industry in the global economy. But mobile communications even compared to other directions of Telecom are developing a leading pace.
Back in 2003 the total number mobile phones The planet exceeded the number of stationary devices connected to wired general networks. In some countries, the number of mobile subscribers has already been greater than the number of residents in 2004. This means that some people used more than one "mobile" - for example, two cell phones serviced from different operators, or a phone for voice and wireless modem for mobile Internet access. In addition, more and more modules wireless communication It was required to ensure technological communications (in these cases, subscribers are not people, but specialized computers).
Currently, cellular operators provide full coverage of the territory of all economically developed regions of the planet, however, the extensive development of networks continues. New base stations are set to improve the reception in those places where the available network for some reason is no sustainable technique (for example, in long tunnels, on the territory of the metro, etc.). In addition, cellular networks gradually penetrate the regions with a low level of income of the population. The development of mobile technology, accompanied by a sharp cheapening of equipment and services, makes cellular services available to an increasing number of people on the planet.
Cell phone production is one of the most dynamically developing areas of the high-tech industry.
The main telephone service industry is growing and offering accessories for personalization of devices: from original calls (ringtones) to brass, graphic screensavers, stickers on the body, replaceable panels, covers and laces for carrying the device.
Types of phones.
Cellular (mobile) phone is a subscriber terminal operating in a cellular network. In essence, each cell phone is a specialized computer, which is focused, first of all, to provide (in the home or guest network coverage area) of the subscribers' voice communication, but also supports the exchange of textual and multimedia messagesSupplied with a modem and simplified interface. Transfer of voice and data Modern mobile phones are provided in digital form.
Early existing separation of devices on "inexpensive", "functional", "business" and "image" models increasingly loses meaning - business devices acquire the features of image models and entertainment functions, as a result of using accessories inexpensive phones become image, and in imaging Functionality is growing rapidly.
Miniaturization of the tubes, the peak of which came in 1999-2000, ended at quite objective reasons: the devices achieved optimal size, their further decrease makes it uncomfortable pressing the buttons, reading the text on the screen, etc. But the cell phone has become a real art subject: to develop external view The devices are attracted by leading designers, and the owners are provided with ample opportunities to personify their devices independently.
Currently, manufacturers are paying special attention The functionality of mobile phones, and as the main one (the battery life increases, screens, etc.) and their additional capabilities are improved (digital cameras, dictaphones, MP3 players and other "related" devices are embedded).
Almost all modern devices, with the exception of certain models of the lower price range, allow you to load programs. Most devices can execute Java applications, increasing the number of phones using operating systems inherited from PDA or ported from them: Symbian, Windows Mobile for Smartphones, etc. Phones with embedded operating systems are called smartphones (from the combination of the English words "Smart" and "Phone" - "smart phone").
As subscriber terminals today, communicators can also be used - pocket computers equipped with a GSM / GPRS support module, and sometimes EDGE and third generation standards.
Unbellex cell networks.
Cell network subscribers are available a number of non-ring services, the "assortment" of which depends on the capabilities of a particular phone and on the spectrum of the operator's offers. The list of services in the home network may differ from the list of services available in roaming.
Services can be communication (providing various forms of communication with other people), information (for example, reporting weather or market quotes), providing Internet access, commercial (for payment from various products and services), entertainment (mobile games, quiz , casino and lottery) and others (here refers, for example, mobile positioning). Today there are more and more services that are "on the junction", for example, most games and lotteries are paid, games that use mobile positioning technologies, etc. appear.
Almost all operators and most modern devices support the following services:
- SMS - SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE - short transmission text messages;
- MMS - Multimedia Messaging Service - Transferring multimedia messages: photos, videos, etc.;
- automatic roaming;
- determination of the caller's number;
- order and receiving various personification tools directly through cellular channels;
- Internet access and viewing specialized sites;
- downloading ringtones, pictures, information materials from specialized resources;
- Data transfer using the built-in modem (it can be carried out according to various protocols, depending on which technologies support specific apparatus).
Mobile communications in Russia.
There were no civil communication systems in the USSR. With some stretch of "civilian", you can call the Altai mobile telephony system, built on the basis of the MRI-1327 standard, which at the turn of the 1970s was created to provide representatives of the Party, State and Economic Guidelines. Altai is successfully operated and understood. Of course, he cannot compete with cellular networks, but it finds use to solve some highly specialized tasks: providing communication of mobile units of urban emergency services, telephoneization of summer cafes, etc.
The first commercial cellular networks, built according to the NMT standard, were created in Russia in the fall of 1991. Mobile telephony pioneers in our country were the company Delta Telecom (St. Petersburg) and Moscow Cellular Communications. The first call on the cell phone was made on September 9, 1991 in St. Petersburg: Anatoly Sobchak, who then held the post of mayor of the city, called his colleague - mayor of New York.
In July 1992, the first calls were committed in the AMPS network "Beeline".
The first Russian network of the GSM standard, created by MTS, began connecting subscribers in July 1994.
In 2005, in Russia there are three federal cellular operators providing services in the GSM standard: MTS, Beeline and MegaFon. The spectrum and the quality of the telecommunication services offered by them, as well as the rates for them are approximately the same. By 2005, the number of base stations in the networks of leading metropolitan operators in Moscow and the nearest Moscow region were about 3,000, and the area of \u200b\u200bthe coverage area exceeded the area of \u200b\u200bmost European states. In addition to them, there are many local operators and quite effectively work - both the subsidiary structures of the "big triple" and independent companies.
Operators are actively developing the market, increasing the coverage of their networks and popularizing the mobile communication among the most different layers of the population. If in the mid-1990 cell phone was available only to representatives of the most secured populations, today almost everyone can use mobile communications. Russian operators introduce new services in their networks and offer services built on them, often even ahead of most European companies. Currently, all three federal GSM operators conduct preparatory work to deploy third-generation commercial networks.
In addition to the GSM networks of federal and local cellular operators in Russia, the networks of other standards continue to be operated: DAMPS, IS-95, NMT-450, DECT and IMT-MC-450. The last standard has federal status, and built on its main network (for example, Skylink) are developing very actively. However, neither on the area of \u200b\u200bthe coating, or by the number of subscribers of the network of all standards other than GSM, not a prominent competition of the leading three of federal operators cannot be created.
Literature:
Maryarevsky A., Olevskaya N. Your mobile phone (Popular tutorial). M, "Peter", 2004
Zakirov Z.G., Nadezhov A.F., Faizullin R.R. Cellular communication of the GSM standard. Modern condition, transition to third-generation networks ("MTS Library"). M., "Eco-Trendz", 2004
Popov V.I. GSM standard cellular base ("Engineering Encyclopedia TEK"). M., "Eco-Trendz", 2005
Communication is called mobile if the source of information is either its recipient (or both) is moved in space. Radio communication from the moment of occurrence was mobile. The first radio stations were intended for communication with mobile objects - ships. After all, one of the first devices of radio communications A.S. Popova was installed on the battleship "Admiral Apraksin". And precisely thanks to the radio communications with him, it was possible in the winter of 1899-1900. Save this ship, shouted in the ice in the Baltic Sea.
For many years, for the implementation of individual radio communications between two subscribers, a separate radio channel operating at one frequency was required. Simultaneous radio communications on many channels could be provided by highlighting each channel a specific frequency strip. But frequencies are needed for broadcasting, television, radar, radio navigation, military needs. Therefore, the number of radio channels was very limited. It was used for military purposes, governmental communications. So, in cars used by members of the Politburo of the CPSU Central Committee, mobile phones were installed. They installed in police cars and radiotaxi. In order to mobile connection I became a mass, it took a new idea of \u200b\u200bher organization.
Each cell must be serviced by a basic radio transmitter with a limited range and fixed frequency. This makes it possible to reuse the same frequency in other cells. During the conversation, the cellular radiotelephone is connected to the base station with a radio channel, which is transmitted by a telephone conversation. The sizes of the cells are determined by the maximum range of the radio telephone apparatus with the base station. This maximum range is a cell radius.
The idea of \u200b\u200ba mobile cellular connection is that by no longer coming out of the zone of a single base station, the mobile phone falls into the zone of action any neighboring right up to the outer border of the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe network.
For this, systems of the antennas-repeaters, overlapping their "honeycomb" - the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe Earth. In order for the connection to be reliable, the distance between two adjacent antennas should be less than the radius of their action. In cities it is about 500 m, and in the countryside - 2-3 km. Mobile phone can receive signals immediately from several repeater antennas, but it is always configured to the most powerful signal.
The idea of \u200b\u200bmobile cellular connection was also to apply computer control over the telephone signal from the subscriber when it moves from one cellular cell to another. It is computer control that has allowed the mobile phone to switch the mobile phone from one intermediate transmitter to another for a thousandth. Everything happens so quickly that the subscriber simply does not notice it.
The central part of the mobile system is computers. They find a subscriber who is in any of the cells and connect it to the telephone network. When the subscriber moves from one cell to another, they transmit subscriber from one base station to another, and also connect the subscriber from the "foreign" cellular network to "its" when it turns out to be roaming (which is carried out in English means "travel" or "vagrancy").
Operation of the first NMT-450 cellular cell system (Nordic Mobile Telephone), designed to work in the 450 MHz range, began in 1981 in Sweden, Iceland, Denmark, Norway, Finland and Saudi Arabia. Then the operation of the system communication systems in Europe and Southeast Asia began. In 1985, on the basis of this standard, the standard of the NMT-900 range of 900 MHz was developed, which made it possible to increase the subscriber capacity of the communication system. Such standards were introduced in the United States, France and the UK.
However, all these standards are analog and refer to the first generation of cellular systems. They use an analog method of transmitting information using frequency (FM) or phase (FM) modulation, as in conventional radio stations. This method has a number of significant drawbacks, the main of which are the ability to listen to conversations by other subscribers and the impossibility of combating the fading signals when the subscriber moves and under the influence of the landscape and buildings. The overload of frequency bands caused interference with conversations.
Therefore, by the end of the 1980s. The creation of a second generation of cellular systems based on the database of digital signal processing methods has begun. In 1990, the GSM-900 standard was developed for the 900 MHz band, which is decrypted as Global System for Mobile Communications. And in 1991, a standard for a range of 1800 MHz was developed on the basis of GSM. Such standards were adopted in the United States and Japan.
In Russia analog systems The cellular communication based on the NMT-450 standard appeared late for 10 years, but the digital systems based on the GSM standard are late for only three years. NMT and GSM standards are approved in our country as federal. In Moscow, cellular networks are most actively developing on the basis of the GSM digital standard, and in the regions - analog networks. GSM standard systems in Russia are most actively promoted in the market three operators - MTS, Beeline and MegaFon. Today, more than 70% of all cell phones in the world work on the basis of this standard. Russia fell to favor with the introduction of cellular communications. We immediately adopted the digital GSM standard. Many modern cell phones are equipped with high-speed Internet access to GPRS (General Packet Radio Service).
Personal cellular mobile communication is becoming increasingly popular, especially in young people. The total number of its users in the world exceeds 600 million subscribers.
An important advantage of mobile cellular communication is the ability to use it outside the general zone of its operator - roaming. For this various operators Agree on the mutual possibility of using their zones for users. The subscriber, leaving the overall zone of his operator, automatically switches to the zones of other operators, even when moving from one country to another, for example, from Russia to Germany or France. Either, being in Russia, the user can call on cellular communications to any country. Thus, cellular communication provides the user with the opportunity to contact the phone with any country, wherever he is.
6.3.1. Cellular network organization
Cell phones ceased to be luxurious and production necessity. They enter our daily life, actively changing both the style and the content of our everyday life. The main idea of \u200b\u200bthe organization of the cellular telephone network is extremely simple. The entire served territory is divided into pieces-cells in which there are base stations connecting mobile phones with each other and with an external world. On the map, such a network of mobile communications resembles beesh cells, from where and the name of this type of telecommunications has come from. Phones in neighboring honeycombs do not interfere with each other, because they work at different frequencies, but we simply do not hear each other thanks to the fact that the earth is round, and radio wave, spreading, faded.
The base station with antennas and the handset in the hands of the subscriber is always close to each other and work at minimum facilities, so the phone becomes truly mobile, compact and light. Basic stations are connected to a high-speed line of communication, for which our conversations and come to the cellular operator. Having gathered on a head mobile station, all calls are charged and commutated with recipients. Naturally, cellular operators have access to the public telephone network, and the call, if it passes outside this network, starts his journey through earthlines.
Thanks to a single control, when moving from a cell to the cell phone, the phone is automatically transmitted to maintain a new base station. The process of transferring the service is accompanied by a change in the working frequency and takes some time, almost imperceptible when talking.
Mobile phone has no constant registration, and it has to be periodically registered on the network, respectively, the cellular operator even during roaming (i.e. when his subscriber travels through someone else's territory) knows where it is located on the connection to the connection, and when requesting confirms the platform The owner of the phone.
6.3.2. Analog cellular standards
Having a lot of general, the cellular communication system is significantly different from each other and, first of all, they use the analog or digital form of information transmission. At first, all systems were analog, and devices are very similar to ordinary coherent rates. Two such systems are most widely spread: American AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone Service) and European NMT (Nordic Mobile Telephone). Today, they still successfully work on the extensive territories of small-populated areas of large countries, when the density of callers is small. These standards have limited capacity and do not allow more than half-length a person at the same time emerge into connection within one cell.
AMPS operates in the range of 800 MHz, NMT-450 - respectively, near 450 MHz, and the NMT-900 is actively used in the Scandinavian countries - about 900 MHz. In NMT, the maximum cell radius can be 40 km, in AMPS it is not more than 20 km. The output power of mobile tubes in NMT-450 reaches 2-3 W, in AMPS does not exceed 0.6 W, for stationary and automotive versions in NMT-450, it can reach 15 W, and the base station is 50-100 watts.
The beep in analog networks is not subject to essential processing, and the communication delay is only a few tens of milliseconds under local calls. Accordingly, the sound of a human voice in such phones looks most naturally and habitual. Characteristic for analog networks noises and interference is largely similar to the typical for wired phones of the roots and cod.
In analog cellular systems, the confidentiality of telephone conversations is fully open, and curious competitors can freely listen to their conversations that are interested in, not only sitting in the car under the office windows, but also in a couple of quarters from the observation facility. Moreover, "improved" models of analog phones, capable of intercepting identification numbers of legitimate users of cellular networks appeared immediately. And illegal apparatus calling for someone else's account was pretty intellectual, and before going to the air, checked if the one who pays for them in touch.
Theft so spread in the world of analog cellular communication, that equipment manufacturers had to urgently complicate the procedure for identifying their subscribers. And today the problem of twins, at least in NMTI, is solved. However, the ability to listen even when the "encryption" is turned on.
Roaming in cellular networks is possible only within the range of your chosen standard, since phones operating in different standards are incompatible. There, where there is a necessary network, there is a so-called semi-automatic roaming, requiring the owner's participation to select desired code countries.
NMT standard phones are still quite recently largely larger than their fellow mobile communications, but today thanks to the success of electronics only the retractable antenna sometimes gives the fact that this is an analog standard device.
In the US, it was very quickly faced with the fact that the analog standard cannot provide all those wishing to communicate. And the new almost completely digital D-AMPS standard (Digital Advanced Mobile Phone Service), which came to the change of AMPS, with the previous maximum cell radius of 20 km raised the number of simultaneously going to the cell of conversations up to three hundred. It was a step that significantly improved the confidentiality of telephone conversations and removed the problem of twins. The transition to the digit, of course, a little affected by speech. This standard allows you to safely ensure stable mobile communications not too tightly located subscribers. He did not become an international standard, so traveling with such a telephone around the world, not everywhere it will be possible to communicate.
In the world, 9 analog standards operating at different frequencies and non-compatible with each other were developed and implemented. Now we successfully work two of them: Scandinavian NMT and American AMPS, and both are used in our country.
6.3.3. Evolution to digital standards
Digital standards with the ability to organize a radius from 0.5 to 20-30 km today 4: American D-APS and CDMA, Global European GSM and Japanese Japanese JDC (Japan Digital Cell).
It is always harder to pioneers, and today, to resist afloat, cellular operators working in NMT and D-AMPS, have not only reduced prices, but also to offer services that the data initially did not assume. Automotive star, identification, voice mail, conference call, data transfer, and even work on the Internet today has become available not only to modern digital standards.
Wide popularity of cellular networks forced developers seriously think about increasing their capacity and standardization throughout the entire planet. Since only when the phone is unified, you can safely travel around the world, remaining in touch with the services of automatic roaming. By this time, the beginning of the 90s, it was already clear that the solution of these two tasks is possible only when moving to digital methods for transmitting speech and communicate.
The development of the global standard was engaged in both Europe and America. The old and new light went a little different ways, and in the end there are two standards working not only at different frequencies, but also using fundamentally different ways of separating at the same time ringing subscribers. Americans in the same frequency band, where AMPS and D-AMPS have been working before, since 1995, the CDMA implementation has begun (Code Division Multiple Access). With the same size of the cell and the same basic infrastructure, the transition to a new standard increased the number of simultaneously callers to a thousand to a thousand, increased the economy of the devices, significantly improved the confidentiality of the negotiations and excluded the problem of twins.
Each CDMA phone has its own individual identification number, and change the device without the participation of the cellular operator is simply impossible. Apparently, including therefore, the cloning messages (i.e. duplication) of this type of phones have not yet been reported. A notebook with numbers and your personal organizer is in an integral phone memory, and, changing the phone, you will have to overwrite all useful information.
Digital systems pay a lot of attention to speech coding, because without compression of the information flow, digital systems will not benefit from the number of subscribers served. The computational capabilities of the telephone microcomputer responsible for encoding and decoding speech is far from any Pentium, and therefore does not comply with the quality of voice transmission in digital mobile communications systems, and admire the fact that the votes of various peoples of the world are transmitted so recognizable.
6.3.4. CDMA and GSM.
CDMA has the highest data transfer rate (14.4 kbps) and enough good quality Sound. The devices operating in this standard are quite miniature and are held long enough. This standard today is widespread in North America and South Korea. In our country, there are also operators who have chosen this standard, however the prevalence of such networks is still small, and potential roaming is strongly limited (and in a situation where this connection is licensed only as wireless, and legally impossible).
The most popular cellular type today is definitely GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications). This European Digital Global Mobile Standard, starting in 1991 in Europe, today de facto has become the most popular standard in the world. It very quickly spreads through our planet, and today in almost all countries, having a GSM phone in the hands, you can calmly call and answer calls, as if you are at home. GSM was developed taking into account the many years of experience of cellular networks, focused on universal use and makes a substantial modification without changing the main functions.
In GSM, the cell radius can reach 35 km, and possibly up to thousands of simultaneous calls. The maximum pulsed power of mobile tubes does not exceed 1 W, although for stationary and automotive phones, it can reach up to 20 W. The devices of this standard are the miniature today and longer are held in touch and in a state of waiting for a call.
Digital communication systems provide clean and without interference sound, only a bit distorting the timbre and intonation of speech. Only with weak levels of the signal and unstable communication is the situation when the phone swallows pieces of words. Winning in the output power and bandwidth when switching to a digit is so significant, and the intelligibility of speech suffers so little, which can definitely have to forgive the phone digital processing of the human voice.
With a conversation, we approximately half the time are silent, listening to the interlocutor. Digital systems actively use this circumstance, almost completely turning off the transmitter in speech pauses, trying not to clog the ether and saving the battery. And so that there is no ringing silence in the speaker's ears, the phone at that time sues the "comfortable noise" speaker, resembling typical sounds at the end of the "wire".
The essential listening of GSM negotiations is difficult, here the developers have tried from the soul. And it's not just in the complex form of the signals used and the closedness of encryption algorithms, but also in the fact that the coding procedure changes all the time, and each new call has its own key.
An interesting step in the struggle for the density of callers was the introduction of GSM 1800, significantly increased bandwidth due to the transition to smaller cells and expansion of the frequency range. Judging by the experience of exploitation of such networks in the largest megalopolis, this step completely removes the problem of network overload even with the magnitude of the population.
All over the world, GSM operates at a frequency of 900 and 1800 MHz, but not only in America. The Federal Commission on Radiocommunication found free and sold operators only a small section of the spectrum in the 1900 MHz region, and there was an American GSM 1900. And in this range there can be both GSM and CDMA and even D-AMPS cellular operators. Today, not only "worldwide" phones operating at 1800 and 1900 MHz are produced today, but also truly omnivorous "Tri-Bunded", who know how to communicate in all three GSM bands.
Cellular networks and the Internet are largely similar to each other, and it is no coincidence that almost all GSM phones have WAP browsers and are actively discussed by projects of the new World Cellular Standard, which will have a significantly higher data transfer rate and ensure quite comfortable work in the World Wide Web due to wider Working Station and Enlarged to GSM and CDMA Pattern Transfer, Images and Data. Today, such a superstructure over GSM in the form of GPRS technology has already been mastered by both Moscow operators and the speed of 40.2 kbps is reached on the reception.
The GSM phones use a replaceable module that is responsible for identifying the subscriber - the so-called SIM card (Subscribe Identity Module). This small chip is not only responsible for noting anyone to call for your money, but also contains extensive memory capable of keeping up to 255 rooms and names of your acquaintances. Accordingly, having rearranged the SIM card from one GSM phone to another, transfers not only a notebook, but also your phone number, to which now there will be in fact another phone.
Personalization of communication means is a rapid pace, and today you can already feel safe from the concept of "working" and "home" phone to the concept of "personal individual telephone number", which is always with you. The most logical solution of this task is the use of SIM cards. The versatility of this small chip allows you to use it in all new, ready-to-launch and developed both cellular and satellite systems Communication.
The range of services provided today by GSM operators is most extensive, and it is continuously replenished. Short SMS text messages (Short Message Servic) and the ability to work on the Internet directly from the keyboard of the phone using a WAP browser, data transmission and faxes (speed 9.6 kbps), conference and call forwarding, information services (prices, Weather, addresses, phone numbers) and the formation of various groups of users - this is not a complete list of the capabilities that the owner of the GSM phone gets.
The section of cellular standards has already been completed, and almost all operators chose some one type of communication. In our country today there are several dozen cellular operators serving almost two million users. Moscow operator "BI LINE", deploying its D-APS network, did not introduce in the same CDMA range, and took up the European GSM 1800. The other MTS operator began with work in GSM 900, and now they both make the main bid on the two-band GSM 900/1800. The oldest Russian cellular network of MCCs together with Sothel continues to cover the immense expanses of our Motherland with the NMT-450i standard, thinking about digitalization. Regional operators successfully master all cellular standards, including CDMA. The Moscow network Sonyet chose CDMA while in stationary, but in perspective, naturally, in a mobile form.
And if the operators provide services in different standards, then manufacturers try to maximize the capabilities of cell phones, making them more and more functional and multi-standard. The union in one case of satellite, cellular and office radio telephone today is in full swing, and in the XXI century. It will be quite realistic in the desert to call on the satellite channel, in the city - on Cell, and in the office - on the local Radio PBX, and all this will happen on one device and the single personal number of the owner of the phone.
Leading manufacturers of cell phones are focused on a single European standard - GSM. That is why their equipment is technically perfect, but relatively inexpensive. After all, they can afford to produce huge parties of phones that are selling.
A convenient addition to the cell phone has become the SMS short message system (Short Message Service). It is used to transfer short messages directly to the telephone of the modern GSM digital system without the use of additional equipment, only with a numeric keypad and a cell phone screen display. Reception of SMS messages is also made on the digital display, which is equipped with any cell phone. SMS can be used in cases where the usual telephone conversation is not the most convenient type of communication (for example, in a noisy crowded train). You can send your phone number to an SMS. Due to the low cost SMS is an alternative to telephone conversation. The maximum value of the SMS message is 160 characters. You can send it in several ways: a call to a special service, as well as using your GSM phone with the send function, using the Internet. SMS system can provide additional services: send to your gSM phone Currency exchange rate, weather forecast, etc. Essentially, the GSM phone with the SMS system is an alternative to the pager.
But the SMS system is not the last word in cellular communication. In the most modern cell phones (for example, Nokia), the Chat function appeared (in the Russian version - Dialogue). With it, you can communicate in real time with other owners of cell phones, as is done on the Internet. Essentially, this is a new type of exchange of SMS messages. To do this, you make a message to your interlocutor and send it. The text of your message appears on the displays of both cell phones - your and your interlocutor. Then he answers you and his message is displayed on displays. So you are driven by an electronic dialogue. But if your interlocutor's cell phone does not support this feature, it will receive ordinary SMS messages.
There are also cell phones with high-speed Internet access support via GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) - a batch data standard for radio channels, in which the phone does not need to be "dialing": the device constantly supports the connection, sends and receives data packets. Cell phone devices with a built-in digital camera are available.
According to the research company Informa Telecoms & Media (ITM), the number of mobile users in the world in 2007 is 3.3 billion people.
Finally, the most complex and expensive devices are smartphones and communicators combining cell phone and pocket computer.
6.3.5. SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE messaging technology (SMS)
Short Message Service (SMS) is today the most common and used way to send and get short messages by mobile GSM standard. SMS has proven itself as a means of communications in the direction of a person - a person and when sending messages that are mainly informational in nature, from the server to the subscriber and between servers.
SMS is provided by the SMS Center (Short Message Service Center or SMSC), which acts as a data bank where messages are stored, and the driving agent that transfers them further. Short messages are sent along the same cellular channel as telephone calls. And in the case of a network providing packet data transfer, messages can be sent even directly during the call on the phone.
In specifications to standard short messages, it is indicated that it cannot exceed 160 characters. Theoretically, the message can be 255 times more, but unfortunately, none of the existing telephone sets can save such a number of information. On average, their memory is designed for only four full messages.
6.3.6. MULTIMEDIA MESSAGE SERVICE (MMS)
MMS refers to a new generation of mobile messaging solutions. Until now, the non-standardized this service promises adding phones a lot of functions that cannot provide EMS.
The MMS standard is designed for GPRS networks, which, unlike easier GSM, have a constant connection to the network, higher throughput and the possibility of packet data transfer, which together with more powerful devices and provides the transition to multimedia messages.
MMS is based on SMS and E-mail standards. He included the best from both systems, and as a result, it turned out a "hybrid" standard optimized for use with mobile devices. This allows you to simplify the integration process with existing systems, applications and, most importantly, users. One of the advantages of the new standard is that when sending a message, both phone numbers and email addresses can be used.
Multimedia Message Service Standard allows you to include text, pictures in jPEG formatCompressed via AMR audio file encoder, SMS-message hidden inside MMS.
In the future, MMS is planned to add support for video formats and various "surcharges", such as Synchronized Multimedia Integration Language (SMIL), which will allow representing mediadata in structured form.
Just as SMS requires a certain service center for storing and sending messages, the MMS requires a service center to manage multimedia messaging.
MMS-Center (in the documentation it is called MMS Relay / Server) is responsible for the following task set:
Getting and sending media messages with and on mobile devices;
Converting media formats depending on the capabilities of the telephone set to which the message is sent;
Generation of invoice information;
Getting and shipping messages with and foreign MMS centers;
Receiving and delivery of messages with and on external systems, such as email;
Receiving and delivery of messages to external providers providing additional services.
Mobile cellular communication
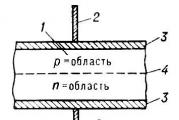
cellular - one of the types of mobile radio, which is based on cell network. Key feature It is that the total coverage area is divided into cells (honeycombs), which are determined by the coating zones of individual base stations (BS). The cells partially overlap and together form a network. On the ideal (smooth and without development) the surface of the coating zone of one BS is a circle, so the network composed of them has the type of honeycomb with hexagonal cells (cells).
It is noteworthy that in the English version the connection is called "cellular" or "cellular" (Cellular), which does not take into account the hexagons of the cell.
The network is separated in the space of receptions operating in the same frequency range, and commuting equipment that allows you to determine the current location of mobile subscribers and ensure the continuity of the connection when the subscriber is moved from the area of \u200b\u200bone transceiver to the other area of \u200b\u200baction.
History
The first use of mobile telephone radio communications in the United States refers to 1921: Detroit police used one-sided dispatching in the 2 MHz range to transfer information from the central transmitter to receivers installed on automaints. In 1933, the New York Police began to use the bilateral mobile telephone radio system also in the 2 MHz band. In 1934, the US Federal Communications Commission allocated 4 channels for telephone radio communications in the range of 30 ... 40 MHz, and about 10 thousand police cars were already telephone radio communications. All these systems used amplitude modulation. Frequency modulation began to be applied from 1940 and by 1946 completely supplanted amplitude. The first public moving radiotelephone appeared in 1946 (St. Louis, USA; Bell Telephone Laboratories), it used the range of 150 MHz. In 1955, a 11-channel system began to operate in the 150 MHz range, and in 1956 - a 12-channel system in the range of 450 MHz. Both of these systems were simplex, and a manual switching was used in them. Automatic duplex systems began to work accordingly in 1964 (150 MHz) and in 1969 (450 MHz).
In the USSR in 1957, the Moscow engineer L. I. Kuryovovich created an experimental sample of the wearable automatic duplex mobile radio telephone LC-1 and the base station to it. Mobile radiotelephone weighed about three kilograms and had a radius of 20-30 km. In 1958, Kupriyanovich creates advanced models of the apparatus weighing 0.5 kg and the size of a cigarette box. In the 60s, Hristo Bochwar in Bulgaria demonstrates its prototype of a pocket mobile radio telephone. At Interorghechnika-66 exhibition, Bulgaria presents a kit for organizing local mobile communications from RAT-0.5 pocket mobile phones and the RATTS-10 base station, which provides connecting 10 subscribers.
At the end of the 50s in the USSR, the development of the Altai automotive radiotelephone system begins, introduced into trial operation in 1963. The Altai system originally worked at a frequency of 150 MHz. In 1970, the Altai system worked in 30 cities of the USSR and a range of 330 MHz was allocated for it.
Similarly, with natural differences and at a smaller scale, the situation in other countries has developed. So, in Norway, public telephone radio communications was used as marine mobile communications since 1931; In 1955 there were 27 coastal radio stations in the country. Ground mobile communication began to develop after the Second World War in the form of private hand-switched networks. Thus, by 1970, mobile telephone radio communications, on the one hand, has already been widely widespread, but on the other, it clearly did not have time for rapidly growing needs, with a limited number of channels in rigidly defined frequency bands. The output was found in the form of a cellular system, which made it possible to dramatically increase the capacity due to the reuse of frequencies in the system with a cellular structure.
Of course, as it usually happens in life, individual elements of the cellular system existed before. In particular, some similarity of the cellular system was used in 1949 in Detroit (USA) by the Taxi Dispatcher Service - with repeated frequencies in different cells when manually switching channels by users in the places specified in advance. However, the architecture of the system, which today is known as a cellular system, was set out only in the technical report of the Bell System, submitted to the US Federal Communications Commission in December 1971 and from this time the development of the cellular communications actually, which became truly triumphal since 1985 G., in the last ten with a small years.
In 1974, the US Federal Communications Commission adopted a decision on the allocation of frequency bands at 40 MHz in the 800 MHz band; In 1986, another 10 MHz in the same range was added to it. In 1978, tests of the first experienced cellular system for 2 thousand subscribers began in Chicago. Therefore, 1978 can be considered a year of the beginning of the practical application of cellular communication. The first automatic commercial cellular system was also put into operation in Chicago in October 1983. Aperican Telephone and Telegraph (AT & T). In Canada, cellular communication has been used since 1978, in Japan - from 1979, in Scandinavian countries (Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Finland) - from 1981, in Spain and England - from 1982 as of July 1997 M. Cellular communication worked in more than 140 countries of all continents, serving more than 150 million subscribers.
The first commercially successful cellular network was the Finnish AutoRADIOPUHELIN (ARP) network. This name is translated into Russian as a "car radio telephone". Launched in G., it reached 100% coverage of Finland. The size of the cell was equal to about 30 km, in the city there were more than 30 thousand subscribers. She worked at a frequency of 150 MHz.
Cellular Principle
The main components of the cellular network are cell phones and basic stations. Basic stations usually have on the roofs of buildings and gear. Being included, the cell phone listens to the air, finding the base station signal. After that, the phone sends its own unique identification code. The phone and station support constant radio contacts, periodically exchanged packages. The phone connection with the station can follow an analog protocol (NMT-450) or on digital (DAMPS, GSM, English. handover.).
Cellular networks may consist of basic stations of a different standard, which allows you to optimize the operation of the network and improve its coating.
Cellular networks of different operators are connected to each other, as well as with stationary telephone network. This allows subscribers of one operator to make calls to subscribers of another operator, from mobile phones to stationary and from stationary to mobile.
Operators of different countries may enter into roaming contracts. Thanks to such treaties, the subscriber, being abroad, can make and receive calls through a network of another operator (however, on high rates).
Cellular communication in Russia
In Russia, cellular communication began to be implemented since 1990, commercial use began on September 9, 1991, when in St. Petersburg, Delta Telecom was launched in Russia, the cellular network (worked in the NMT-450 standard) and was performed first Symbolic call on cellular communication by Mayor of St. Petersburg Anatoly Sobchak. By July 1997, the total number of subscribers in Russia amounted to about 300 thousand. For 2007, the main protocols of the cellular communication used in Russia are GSM-900 and GSM-1800. In addition, UMTS work. In particular, the first fragment of the network of this standard in Russia was commissioned on October 2, 2007 in St. Petersburg by MegaFon. The Sverdlovsk region continues to be operated by the cellular network of the DAMPS standard owned by the company's cellular communication "Motive".
In Russia, in December 2008, there were 187.8 million cellular users (by the number of SIM cards sold). The level of cellular penetration (the number of SIM cards per 100 inhabitants) was thus 129.4%. In the regions, without taking into account Moscow, the penetration rate exceeded 119.7%.
The share of the market of the largest cellular operators for December 2008 was: 34.4% at MTS, 25.4% from VimpelCom and 23.0% at MegaFon.
In December 2007, the number of cellular users in Russia increased to 172.87 million subscribers, in Moscow - up to 29.9, in St. Petersburg - to 9.7 million. The level of penetration in Russia - up to 119.1%, Moscow - 176% St. Petersburg - 153%. The share of the market of the largest cellular operators for December 2007 was: MTS 30.9%, VimpelCom 29.2%, MegaFon 19.9%, other operators 20%.
According to the data of the British research company Informa Telecoms & Media for 2006, the average cost of a cellular communication for the consumer in Russia was $ 0.05 - this is the lowest figure of the G8 countries.
IDC based on the study of the Russian cellular communication market concluded that in 2005 the total duration of conversations on the cell phone in the Russian Federation reached 155 billion minutes, and the text messages were sent 15 billion pieces.
According to the research of the J "Son & Partners, the number of SIM cards registered in Russia as of the end of November 2008 reached 183.8 million.
see also
Sources
Links
- Information site about generations and cellular standards.
- Cellular communication in Russia 2002-2007, data of official statistics
| cellular in Russia | |
|---|---|
| Cellular operators | Utel Akos Altayesvyaz Baikalwest Beeline ETK Megaphone Motive MTS NSS NTC Smarts Sky Link Sonnet Sotel SSS Stack GSM Tomsktelecom UUS Digital Expansion |
| Cell phone sales network | Divizion Simfonia Alttelecom Banzai Betalink Euroset Ion Svyaznoy Communication Spectrum Phone Phone Telephone Point Ultra Digitivity Eldorado |
| Cellular standards | D-AMPS GSM IMT-MC-450 IS-95 |